Yes. mRNA vaccines, such as Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, work differently than other types of vaccines, but they still trigger an immune response inside your body. This type of vaccine is new, but research and development on it has been under way for decades.
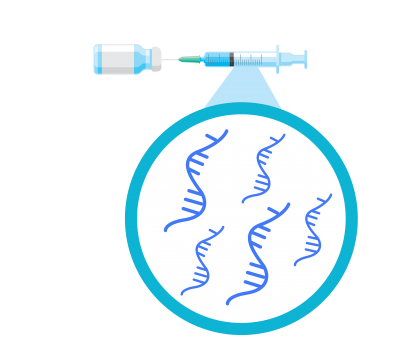
The mRNA vaccines do not contain any live virus. Instead, they work by teaching our cells to make a harmless piece of a “spike protein,” which is found on the surface of the virus that causes COVID-19. After making the protein piece, cells display it on their surface. Our immune system then recognizes that it does not belong there and responds to get rid of it. When an immune response begins, antibodies are produced, creating the same response that happens in a natural infection.
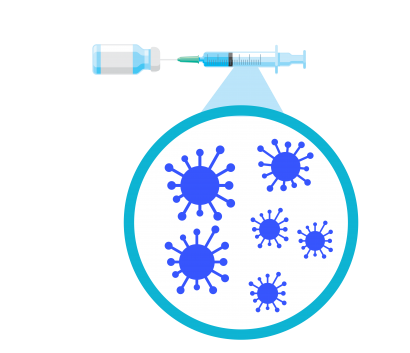
In contrast to mRNA vaccines, many other vaccines use a piece of, or weakened version, of, the germ that the vaccine protects against. This is how the measles and flu vaccines work. When a weakened or small part of the virus is introduced to your body, you make antibodies to help protect against future infection.
Learn more about how mRNA COVID-19 vaccines work.